Page 60 - Flipmag-02
P. 60
W H I T E P A P E R
HAND REVOLUMISATION aestheticmed.co.uk
9
bioresorbable. PCL hydrolyses to hydroxycaproic acid and DURATION OF IMPROVEMENT
water, which is reabsorbed and excreted via a variety of The assessment of hand volume was based on the hand
metabolic pathways. severity scale reported ( ) and is summarised in Table 1.
6,17
CMC gel is absorbed by macrophages over several Four patients with severe volume loss (grade 3) achieved
weeks. A CMC-based filler has been shown to effectively improvement to moderate (grade 2) severity. Ten patients
15
correct nasolabial hollows for up to six months in a with moderate severity (grade 2) improved to mild severity
16
bilateral period comparison study against an HA filler). (grade 1). One patient with moderate volume loss did not
PCL microspheres are not phagocytised but are thought show improvement on clinician’s grade scores four months
to stimulate neocollagenesis via fibroblast activation, after the first treatment but was slightly satisfied with
perhaps by cytokine release during microsphere resorption improvement. She elected to receive a second treatment.
in the skin. Studies in animal model showed initial deposition
of type-3 collagen with later deposition of type-1 collagen. 9
Clinical observations have confirmed that PCL-based
microspheres are well tolerated for facial treatment. One
previous pilot study of hand rejuvenation in five patients
showed improvement of patient and physician reported
10
Global Esthetic Improvement Scale (GAIS) for six months.
Comparative studies have shown that PCL-based fillers,
when compared with a hyaluronic acid filler, showed greater
persistence. 7
MATERIALS AND METHODS
15 female patients aged between 48 and 72 years of skin
type 2 and 3 were evaluated for PCL filler injections to
their hands because of dorsal hand volume loss (Ellansé
typeM, Sinclair Pharmaceutical). They were provided with
informed consent at least five days prior to treatment.
They all had a minimum rating of three on a previously
reported hand aging severity scale. 17 Their hands were
photographed before and following treatment with
consistent photography. Clinical examination of dorsal
hand skin quality recorded severity of rhytides, skin laxity,
and elasticity.
METHODS OF INJECTIONS OF PCL
PCL (Ellansé M) was selected for treatment based on
past personal experience with Ellanse products for facial
10
volume loss (Lowe, NJ personal data and a pilot study).
Hands were cleansed with chlorhexidine gluconate 4%.
Local anesthetic (0.1 ml of 1% lidocaine) was drawn into a
1ml syringe and mixed with PCL filler by luerlock connection
with 20 transfers between the syringes.
Entry points for cannulas were selected to avoid
dorsal hand veins and entry areas injected with 0.3ml of
1% lidocaine with adrenaline. 25G (50mm) cannula with
introducer (SoftFil) was used for all patients. The cannula
was inserted through an introducer to mid to upper
subcutaneous depth and PCL injected using a retrograde
technique while slowly withdrawing the cannula. A total
of 1cc PCL was injected to the dorsal of each hand. The
injected area was then massaged to smooth the area.
Side effects and severity of pain and swelling were noted
over the following five days. Presence of bruising and
swelling was documented.
RESULTS
Results are summarised in Tables 1 and 2. Severity scores
improved in all patients and were recorded as the degrees
6,17
of improvements using the scales previously reported.
This improvement was statistically significant (Fisher
exact test 0.0002. p < .05). Seven of the patients elected
to have a second treatment between the two evaluation
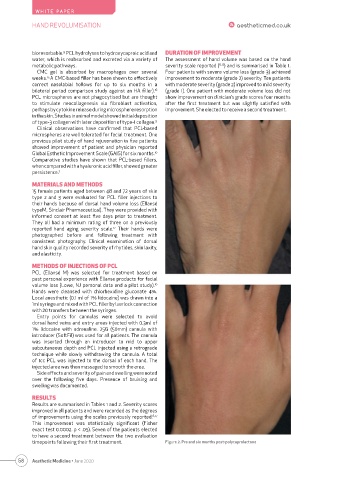
timepoints following their first treatment. Figure 2. Pre and six months post-polycaprolactone
58 Aesthetic Medicine • June 2020