Page 62 - Flipmag-02
P. 62
W H I T E P A P E R
HAND REVOLUMISATION aestheticmed.co.uk
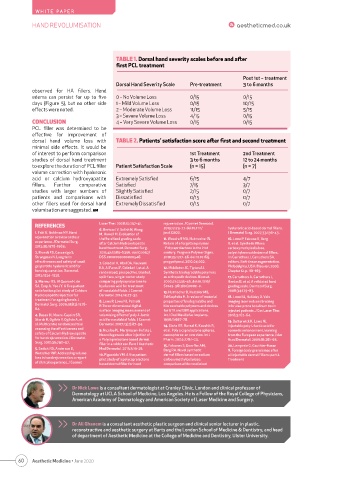
TABLE 1. Dorsal hand severity scales before and after
first PCL treatment
Post 1st – treatment
Dorsal Hand Severity Scale Pre-treatment 3 to 6 months
observed for HA fillers. Hand
edema can persist for up to five 0 – No Volume Loss 0/15 0/15
days (Figure 5), but no other side 1 – Mild Volume Loss 0/15 10/15
effects were noted. 2 – Moderate Volume Loss 11/15 5/15
3 – Severe Volume Loss 4/15 0/15
CONCLUSION 4 – Very Severe Volume Loss 0/15 0/15
PCL filler was determined to be
effective for improvement of
dorsal hand volume loss with TABLE 2. Patients’ satisfaction score after first and second treatment
minimal side effects. It would be
of interest to perform comparison 1st Treatment 2nd Treatment
studies of dorsal hand treatment 3 to 6 months 12 to 24 months
to explore the duration of PCL filler Patient Satisfaction Scale (n = 15) (n = 7)
volume correction with hyaluronic
acid or calcium hydroxyapatite Extremely Satisfied 6/15 4/7
fillers. Further comparative Satisfied 7/15 3/7
studies with larger numbers of Slightly Satisfied 2/15 0/7
patients and comparisons with Dissatisfied 0/15 0/7
other fillers used for dorsal hand Extremely Dissatisfied 0/15 0/7
volumisation are suggested. AM
Laser Ther. 2008;10:237–41. rejuvenation. J Cosmet Dermatol.
REFERENCES 2013;12:73–77. doi:10.1111/ hyaluronic acid-based dermal fillers.
6. Bertucci V, Solish N, Wong
1. Fabi G, Goldman MP. Hand M, Howell M. Evaluation of jocd.12020. J Dermatol Surg. 2007;33:136–43.
rejuvenation a review and our theMerzHand grading scale 11. Woodruff MA, Hutmacher W. 16. Lowe P, Falcone S, Berg
experience. J Dermatol Surg. after Calcium Hydroxylapatite Return of a forgotten polymer R, et al. Synthetic fillers:
2012;35:1978–1984.
hand treatment. Dermatol Surg. - Polycaprolactone in the 21st carboxymethylcellulose,
2. Brandt FS, Cazzaniga S, 2015;41:S389–S396. doi:10.1097/ century. Progress Polymer Signs. polyethylene oxide dermal fillers.
Strangman N. Long term DSS.0000000000000546. 2010;35:1217–56. doi:10.1016/j. In: Carruthers J, Carruthers SA,
effectiveness and safety of small 7. Galadari H, Abel DA, Neuvami progpolymsci.2010.04.002. editors. Soft tissue augmentation.
gel particle hyaluronic acid for KA, Al Faresi F, Galadari I, et al. A 12. Middleton JC, Tiptan AJ. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier; 2008.
hand rejuvenation. Dermatol. randomised, prospective, blinded, Synthetic biodegradable polymers Chapter 12. p. 161–165.
2012;1524–1525. split-face, single-center study as orthopedic devices. Biomat. 17. Carruthers A, Carruthers J,
3. Marmur ES, Al Quaran H, de comparing polycaprolactone to 2000;21:2335–46. doi:10.1016/ Hardas B, et al. A validated hand
SA, Earp A, Yoo JY. A five patient hyaluronic acid for treatment S0142- 9612(00)00101-0. grading scale. Dermatol Surg.
satisfaction pilot study of Calcium of nasolabial folds. J Cosmet 13. Hutmacher D, Hurzeler MB, 2008;34:179–83.
Hydroxyapatite injection for Dermatol. 2014;14:27–32. Schliephake H. A review of material 18. Lowe NJ, Halliday D. Vein
treatment for ageing hands. J 8. Lowe P, Lowe NJ, Patnaik properties of biodegradable and imaging laser reduces bruising
Dermatol Surg. 2009;35(12):1978– R.Three-dimensional digital bioresorbable polymers and devices in bruise-prone botulinum toxin
84. surface imaging measurement of for GTR and GBR applications. injected patients. J Cos Laser Ther.
4. Busso M, Moers-Caprim SR, volumising effect of poly-L-lactic Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2018;3:162–64.
Storck R, Ogilvie P, Ogilvie A, et acid for nasolabial folds. J Cosmet 1996;11:667–78. 19. Butterwick K, Lowe NJ.
al. Multicentre randomised trial Dermatol. 2007;13(2):87–94. 14. Sinha VR, Bansal K, Kaushik R, Injectable poly-L-lactic acid for
assessing the effectiveness and 9. Nicolau PJ, Marijnissen-Hofste J. et al. Poly e caprolactone spheres, cosmetic enhancement, learning
safety of Calcium Hydroxyapatite Neocollagenesis after injection of nanospheres: an overview. Int J from the European experience. J Am
for hand rejuvenation. J Dermatol a Polycaprolactone based dermal Pharm. 2004;278:1–23. Acad Dermatol. 2009;61:281–93.
Surg. 2010;36:790–97.
filler in a rabbit ear. Euro J Aesthetic 15. Falcones S, Doerfler AM, 20. Lemperle G, Gauthier-Hazan
5. Sadick NS, Anderson D, Med Dermatol. 2013;3:19–26. Berg RA. Novel synthetic N. Foreign body granulomas after
Werschler WP. Addressing volume 10. Figuerido VM. A five patient dermal fillers based on sodium all injectable dermal Fillers: part 2.
loss in hand rejuvenation: a report pilot study of a polycaprolactone carboxymethylcellulose: Treatment
of clinical experience. J Cosmet
based dermal filler for hand comparison with crosslinked
Dr Nick Lowe is a consultant dermatologist at Cranley Clinic, London and clinical professor of
Dermatology at UCLA School of Medicine, Los Angeles. He is a Fellow of the Royal College of Physicians,
American Academy of Dermatology and American Society of Laser Medicine and Surgery.
Dr Ali Ghanem is a consultant aesthetic plastic surgeon and clinical senior lecturer in plastic,
reconstructive and aesthetic surgery at Barts and the London School of Medicine & Dentistry, and head
of department of Aesthetic Medicine at the College of Medicine and Dentistry, Ulster University.
60 Aesthetic Medicine • June 2020